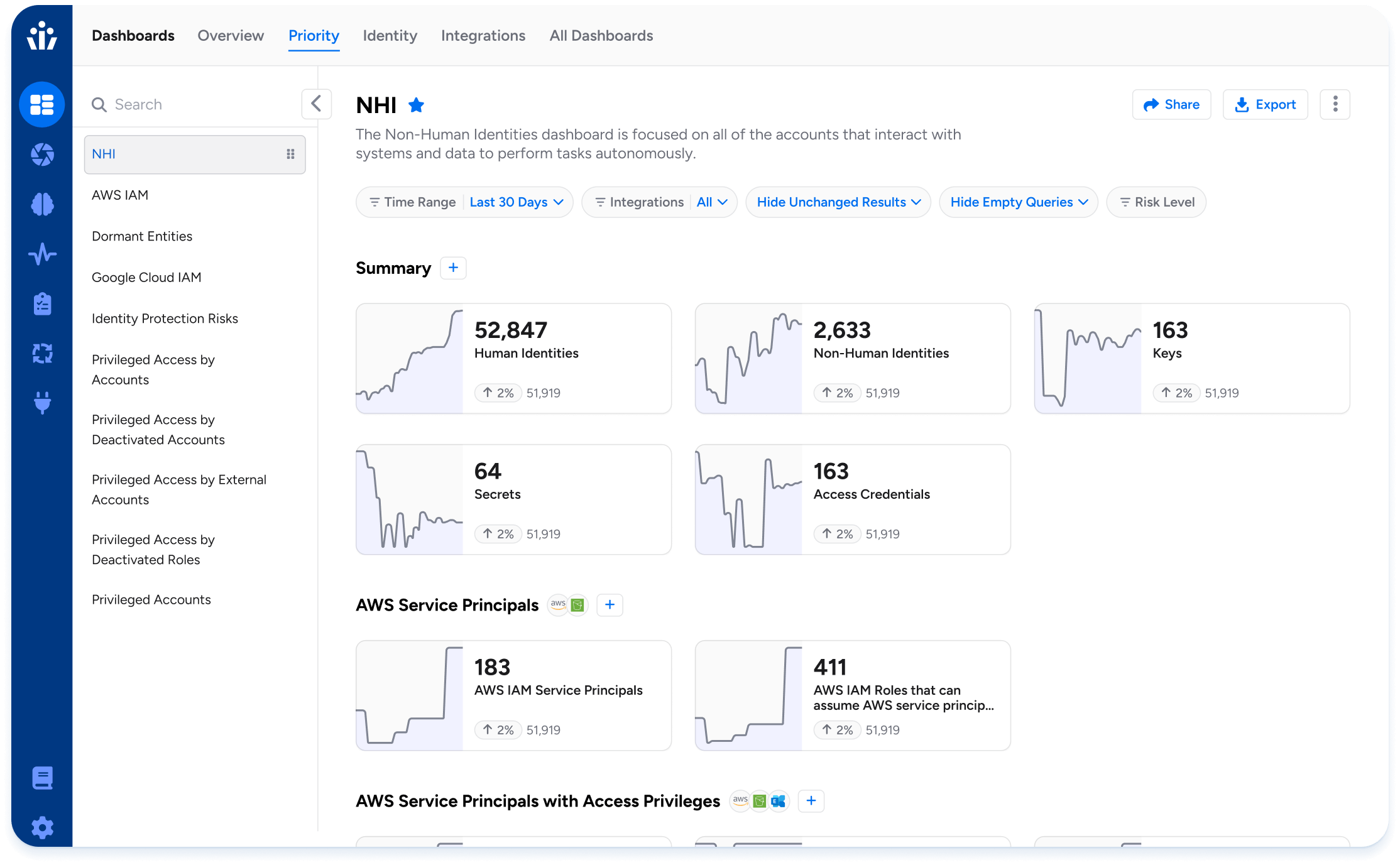
Non-Human Identity Management
Non-human identities (NHIs) are the largest and fastest growing part of your identity attack surface, outnumbering human identities by an average of 17 to 1. Hackers are attacking NHIs because they know they can avoid human-focused security tools like MFA, so your security and compliance strategies must adapt to secure NHIs as first-class citizens.
Challenges in
securing NHIs
Intelligent access
for NHIs
Discover NHIs across your stack
- Discover NHIs efficiently across on-prem, SaaS apps, custom apps, and cloud infrastructure.
- Import data from CMDBs or external spreadsheets to clearly label NHIs and assign human owners.
- Identify “shadow” NHIs not in your secrets manager and bring them in line with your security and governance policies.
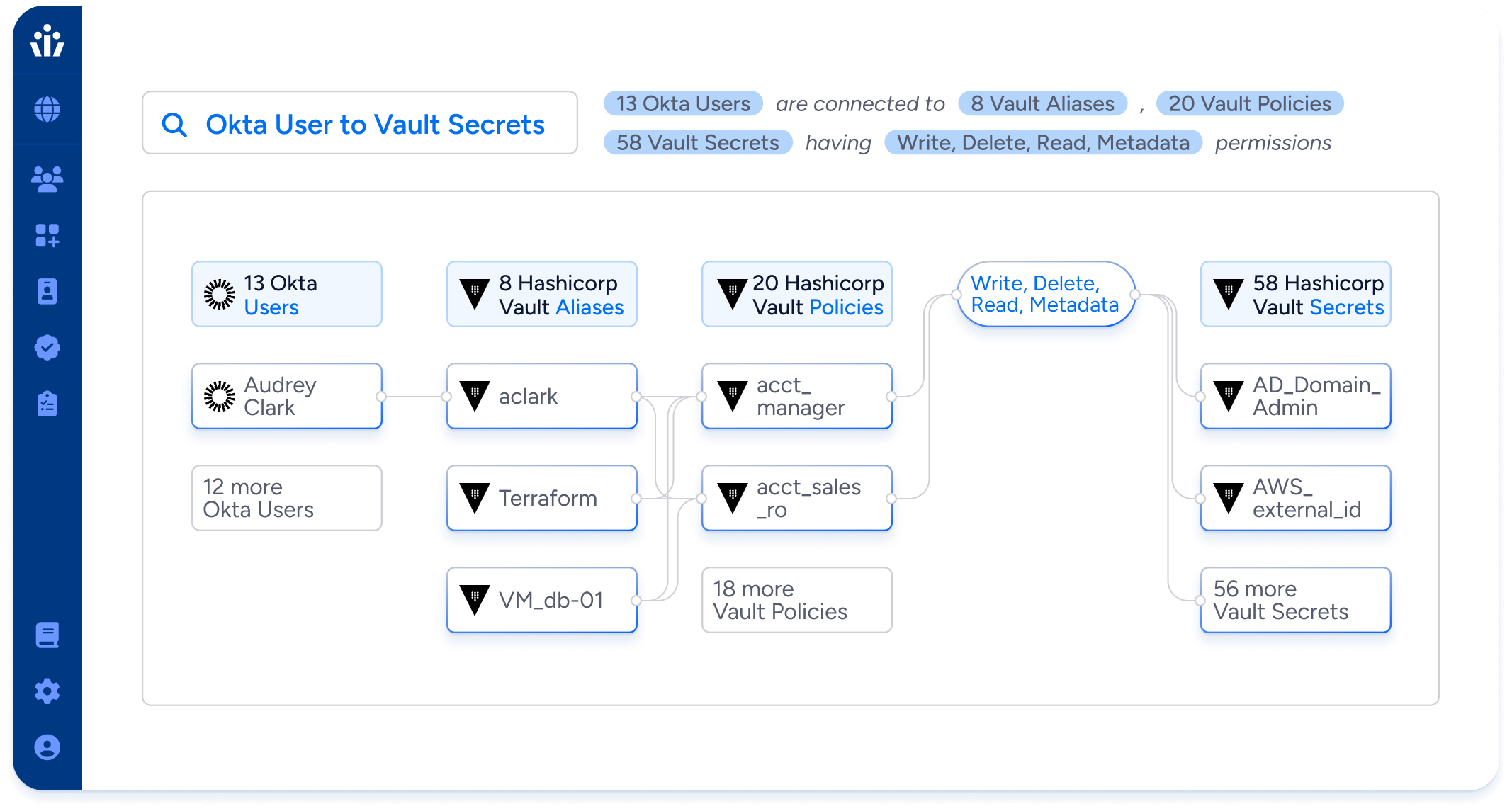
Least privilege for all identities
- Analyze permissions and activity of NHIs to identify and remove unneeded privileges, including admin permissions, without disrupting business-critical processes.
- Eliminate shadow NHIs by identifying and restricting the power to create and provision access to virtual machines, lambda functions, certificates, and secrets.
- Use access requests and role recommendations to create a single streamlined provisioning processes for both human and non-human identities that maintains least privilege.
One platform to govern humans and NHIs
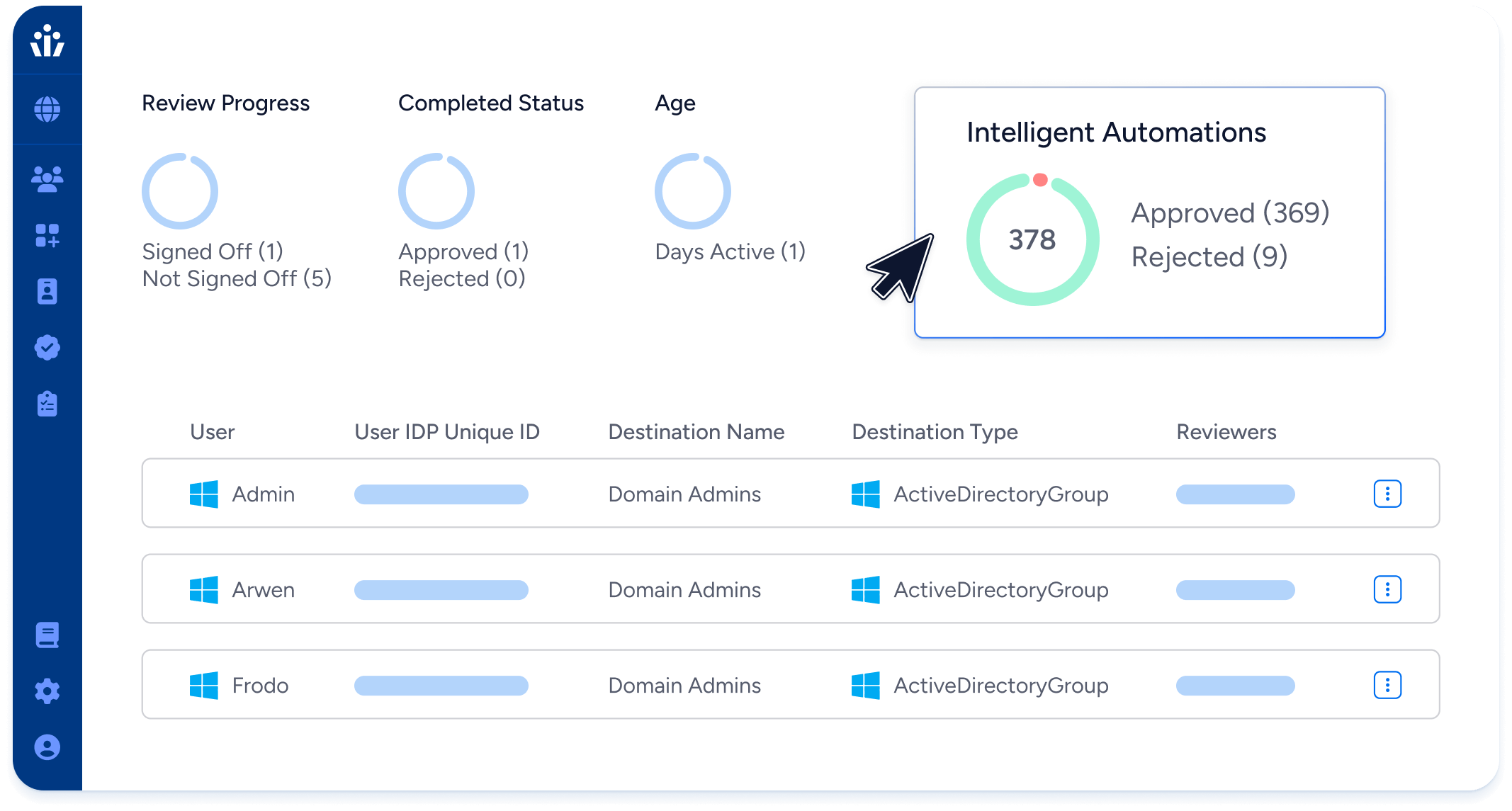
- Run NHI Ownership Certification campaigns to ensure business need, correct ownership, and least privilege.
- Secure NHIs in local accounts, and manage human permissions to enforce a secure NHI Lifecycle.
- Enforce security policies like key rotation for NHIs, and provide useful context to access reviewers, like “Time last rotated” and “Time last used”.
NHI use cases
NHIs impact all aspects of the enterprise. Veza helps you discover, secure, and provision NHIs wherever they are.
Discover NHIs
Find and label which accounts are non-human across 250+ integrations
Identify “clear” NHIs, like service principals and managed service accounts. Use search and filtering to find “likely” NHIs, for example via naming conventions or lack of MFA. Sync NHI labels in Veza with external sources like CMDBs.
Analyze permissions for least privilege
Understand permissions of NHI accounts/keys and right-size to business need
NHIs have been part of Veza’s data model and platform since day one. See all permissions to system resources across all Veza integrations.
Assign human owners
Enables governance and manual key rotation
Use Veza Tags to assign human owners to NHIs. Import ownership data from spreadsheets or other external sources.
Ensure key rotation
Identify login credentials and security/compliance risks.
Associate credentials with NHIs, and capture metadata from integrated systems, like “Time last rotated” and “Time last used”
Access Reviews
NHI owner-driven reviews
Assign reviews of all access to NHIs to their owners for certification. Identify and remove unneeded access.
Activity monitoring
Find dormant permissions to fix excess privilege
Know if NHIs are actually using their permissions in core platforms like Snowflake and AWS. Remove unused access.
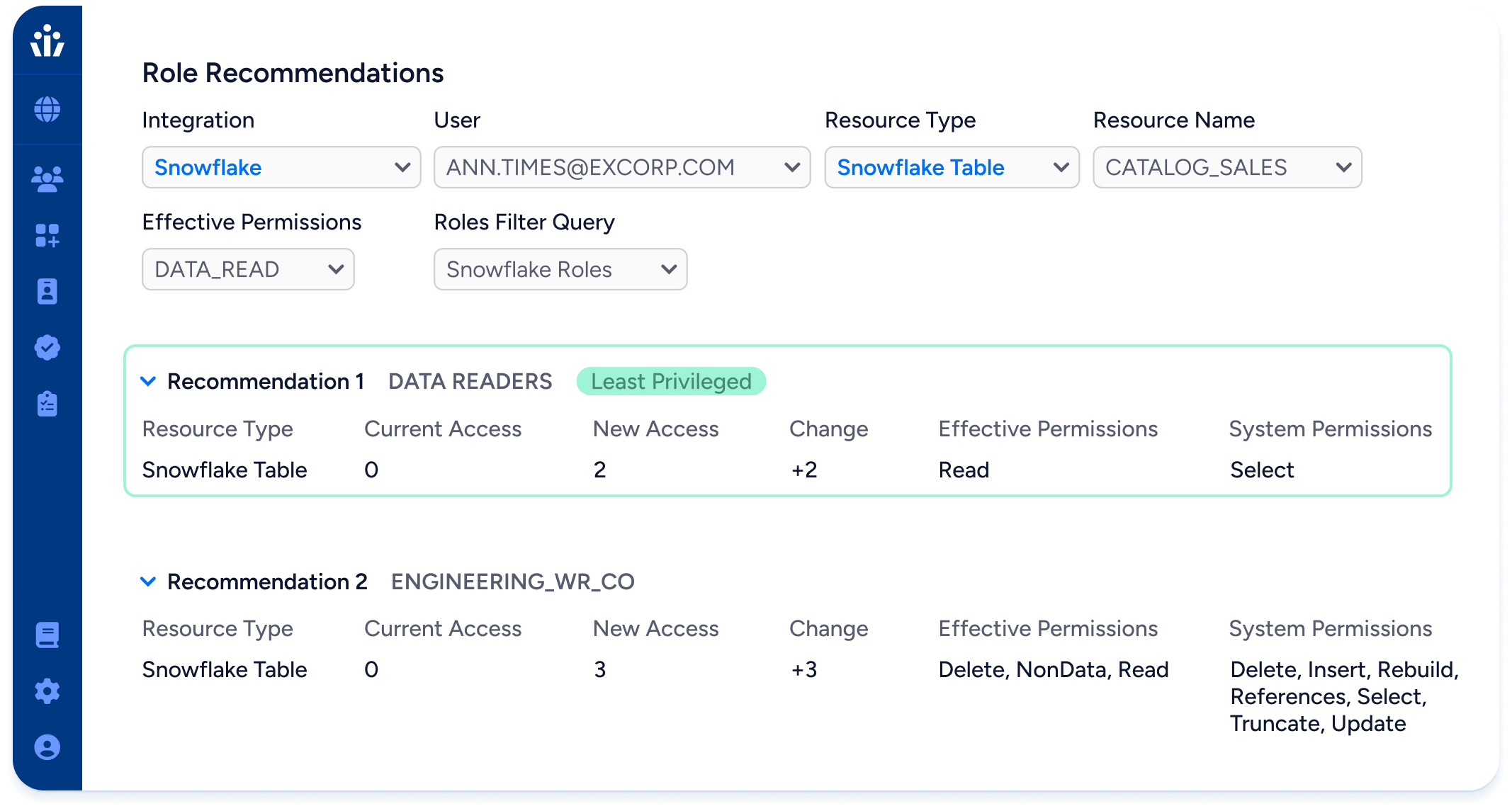
Role recommendations
Create new NHIs that are right-sized to application needs
Optimize the NHI provisioning process to fix over-permissioning at the time of account creation. Eliminate “admin-level” permissions on NHIs where not needed.