Welcome to the Veza September 2025 Product Update! This release advances Veza’s leadership in Identity Security, addressing non-human identity (NHI) security and AI Governance requirements, and deepening automation for all IGA needs, for Access Reviews, Lifecycle Management, Access Request, and Access Hub.
From expanded credential discovery to Access AI explanations and lifecycle automation with Open Authorization API (OAA), this release strengthens the foundation for risk-aware, policy-driven governance across your enterprise. Below you’ll find detailed information on specific updates. As always, please contact your Veza support team with questions and feedback.
Release Highlights
September releases (`v2025.8.25-1` through `v2025.9.29-1`) introduce platform-wide enhancements and features across four focus areas:
Lifecycle Management Advancements
- Secondary Sources of Identity (GA): The ability to support a secondary source of identity to augment or enrich primary identity sources with supplementary identity data.
- Create Access Review Action (GA): Lifecycle Management workflows now support the Create Access Review action, triggering on-demand access reviews during lifecycle events.
- SCIM for Custom Applications: SCIM-compliant applications are now supported as target applications using the Open Authorization API. This allows Lifecycle Management to automate provisioning and deprovisioning for integrations using OAA templates.
- MySQL Database Support: MySQL databases are now supported as target applications, allowing Lifecycle Management to automate provisioning and deprovisioning.
- OAuth2 SCIM Authentication: Authentication to SCIM-based endpoints using the OAuth2 protocol is now supported.
- Workflow Trigger Properties: The execution of Lifecycle Management workflows can be limited to run only when specific identity properties change.
- Why It Matters: Organizations can now enforce least privilege continuously, not just periodically.
Operational Usability and Enhanced Access Reviews
- Slackbot for Access Reviews: Review notifications and reminders can be sent directly to the applicable reviewers in Slack.
- Predefined Question Sets: Require reviewers to answer a standard set of questions for each review row, ensuring consistent decision justifications.
- Persistent “Group By” Settings: Reviewer preferences for “group by” attribute now saved across reviewer sessions.
- Why It Matters: Reviewer experience is enhanced while compliance and security teams save time, improving audit readiness and consistency.
Advanced Non-Human Identity Security
- OAuth and Credential Discovery: Okta OAuth tokens, application client secrets, refresh tokens, and key credentials for complete machine identity governance.
- Azure Key Vault Monitoring: Track key and secret access patterns, rotation events, and usage activities.
- AI Agent Discovery: Salesforce Agentforce and Einstein Bot mapping for service accounts and user permissions.
- Certificate-Based Authentication: AWS Identity Center and IAM Roles Anywhere X.509 certificate discovery.
- Azure AD NHI Expansion: Service principal classification, app registration credentials, and OAuth2 token tracking.
- HashiCorp Vault Key-Level Discovery: KV2 secrets engine and granular key-value pairs.
- Why It Matters: Customers can now visualize, audit, and govern every credential — human or machine — across multi-cloud environments.
Enhanced Risk Intelligence and Query Management
- Improved Query Management: Saved queries sorted by creation date with badge indicators.
- Enhanced SoD Exports: Download full query metadata, including timestamps, risk levels, and exception status.
- One-Click Risk Details: Direct access to contributing queries from risk scores.
- Access AI Side Panel (Early Access): AI-driven analysis alongside your primary workflows.
- Why It Matters: Empower Security teams to move from discovery to remediation, reducing friction between detection and response.
Access Security
Query Management and AI Enhancements
Query Explanations with Access AI (Early Access): Transform complex VQL queries into plain language explanations by clicking the Access AI button in the query details view.
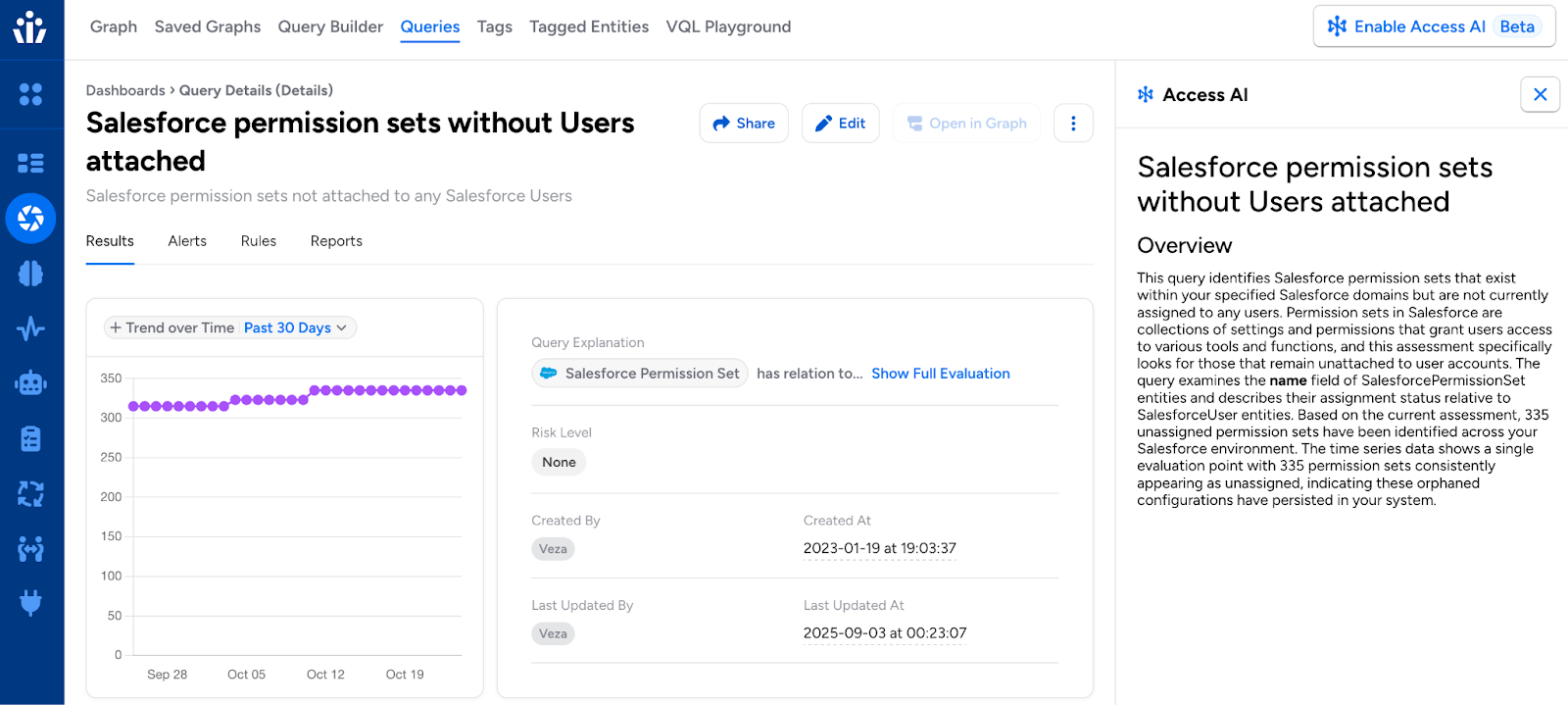
Access AI analyzes query structure and translates technical syntax (such as nested relationships, conditional filters, and entity traversals) into human-readable descriptions of what the query discovers and why it matters.
This helps security analysts understand queries built by others, aids in troubleshooting unexpected results, and supports knowledge transfer across teams. Requires Access AI to be enabled for your organization. Learn more about Access AI.
- Improved Query Management UX: The saved query management interface now defaults to showing the newest queries first, helping teams quickly find their most recent work.
Visual badge indicators mark recently created queries, making it easier to spot new additions when reviewing shared query libraries. Queries with identical names across different teams now display with proper unique identification.
- Monthly Query Export Scheduling: Automated query exports now support monthly cadences alongside weekly schedules, enabling reporting aligned with monthly compliance cycles or board meetings.
Users can now choose which months to run exports and select between the 1st and 15th day of each month to accommodate varying reporting deadlines. Ideal for quarterly access certifications, monthly executive dashboards, or periodic compliance reporting requirements.
- Comprehensive SoD Metadata Exports: When exporting Segregation of Duties violations (or any saved query), the download now includes additional context, making it easier to share compliance reports with auditors or present findings to executives.
- Each export contains the generation timestamp, query configuration details, risk levels, assigned SoD managers, conflicting roles or permissions, exception status with notes, and risk assignee information.
Access Visibility
Advanced Query and Graph Controls
Query Builder Path Type Selection: When investigating access patterns, you can now distinguish between access-granting and structural relationships with the new “Path Type” selector in Query Builder advanced options. This helps security teams answer questions such as “who can access this resource?” separately from “which groups contain this user?”
- Choose Permission paths to trace relationships where permissions are explicitly assigned, for example, a user who has read permission on an S3 bucket through a role.
- Choose Non-Permission paths to discover structural relationships like group memberships, role assumptions, or which databases contain user accounts (relationships that exist without granting specific permissions).
Access Graph Path Controls: When exploring access paths visually in Graph search, you can now control which relationships the graph follows.
- Use Direction Options to trace outgoing paths, incoming paths, or bidirectional relationships.
- Combine this with Path Type Options to display only structural relationships, such as group memberships and role assignments.
Agentic User Visualization: Non-human identities now display with distinct visual markers in Graph search. Service accounts, bots, and API keys are now identified by green badges, with human users distinguished by blue badges. This makes it easier to spot automated identities during incident investigations or when certifying access for machine accounts.
Query Builder Performance Enhancements: Query results now load faster when navigating through large result sets. The Query Builder now utilizes cached data and handles pagination more efficiently, reducing wait times when exploring access patterns across thousands of entities.
Access Reviews
Enhanced Collaboration and Standardization
Veza Slackbot for Access Review Notifications: Reviewers can now receive access review reminders directly in Slack. After configuring the Slack app integration, Veza delivers notifications for review initiation, completion, reviewer changes, due date reminders, and inactivity alerts to the relevant users in their personal Slack workspace. Each message includes a direct link to the review in Veza. You can use Slack alongside email notifications, or switch entirely to Slack-based delivery.
Predefined Question Sets: When configuring an Access Review, administrators can now require reviewers to answer specific questions before they can approve or reject access.
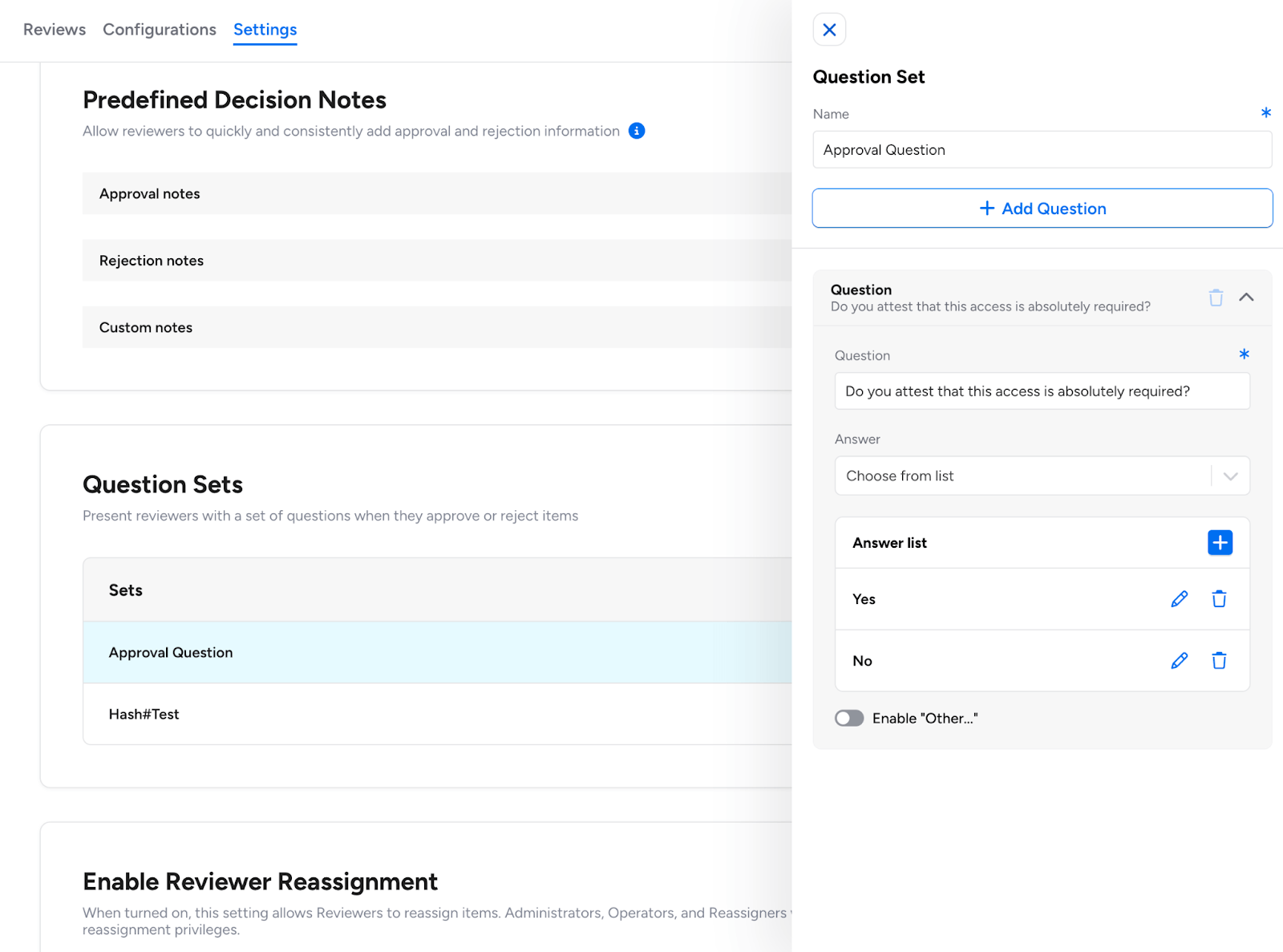
Question sets support multiple-choice options or freeform text responses to standardize how reviewers document their decisions.
Persistent “Group By” Settings: Each user’s preferred way of organizing review line items is now remembered across user sessions. When you group line items by User, Source, Destination, Risk Level, or Status, that selection now persists the next time you open the review.
Default “Group By” Setting: Administrators can now set organization-wide defaults for “group by” using Admin > Set Columns as Default, enabling all reviewers to see a default layout optimized for each review, per review configuration.
Access AI for Review Explainability (Early Access): AI-driven summaries of access reviews now appear in a side panel that slides out from the current view. This enables reviewers to quickly access a summary of key information, such as an explanation of the review and its scope, its status, the number of rows pending sign-off, and the due date.
Activity Monitoring
New Features
Azure Key Vault Activity Monitoring: You can now visualize unutilized access to secrets stored in Azure Key Vault. After configuring an Azure integration with a Log Analytics workspace ID, Veza will extract audit trails showing key and secret access patterns, rotation events, and usage activities. This activity data is now available in Access Monitoring dashboards to identify dormant credentials, unusual access patterns, or keys that haven’t been rotated. Learn more about Activity Monitoring.
Lifecycle Management
New Features
Secondary Sources of Identity (GA): Veza can now combine identity data from a secondary authoritative source of identity (SOI) when building Lifecycle Management policies. For example, you can configure a core HR system as the primary identity source while sourcing manager assignments from a separate departmental database. Secondary SOIs let you enrich identity records with attributes that don’t exist in your primary SOI, enabling workflows that rely on cross-system data.
Create Access Review Action (GA): Lifecycle Management workflows can now automatically trigger the launch of access reviews.
- When configuring a workflow, administrators can now use the Create Access Review action to immediately launch a predefined access review for the user. Review launch options include starting reviews in either an active or draft state, specifying auto-assigned reviewers, and configuring reviewer notifications that are triggered automatically when the review is started.
Expanded Integration and Automation
SCIM Integration for External OAA Applications: Lifecycle Management can now automate user provisioning and deprovisioning for any custom application built with the Open Authorization API (OAA) that implements SCIM 2.0-compliant endpoints for user and group management. This enables automated workflows for nearly any home-grown application, including user creation, group membership management, and account deprovisioning.
OAuth2 SCIM Authentication Support: SCIM integrations now support OAuth2 authentication in addition to bearer tokens, expanding compatibility with modern enterprise applications.
Workflow Trigger on Change: Workflows can now be configured to trigger only on changes to specific source attribute(s). For instance, when configuring a Mover workflow that reassigns access based on department, administrators can now select a trigger attribute such as `department`. The workflow will execute when an individual changes departments, but not when unrelated fields such as ‘phone number’ or ‘address’ change.
MySQL Database Lifecycle Management Support: MySQL databases are now a supported Lifecycle Management target application. This allows automated creation of MySQL users (identified by username and host), assignment or revocation of role memberships using `GRANT`/`REVOKE` operations, and disablement of accounts with `ACCOUNT LOCK` when employees leave.
Enhanced Policy Management and Usability
Access Profiles Usability: The Access Profiles view has been refreshed with improved navigation. The updated layout makes it easier to define and manage how entitlements are assigned to employees based on roles, functions, or locations.
Native Attribute Mapping for Transformers: The policy editor now shows both source properties and Veza-normalized attribute names when configuring transformers. If your HR system contains an attribute ’emp_dept’ but Veza normalizes it to `department’ in the Access Graph, administrators will see both names for easier mapping of data between systems.
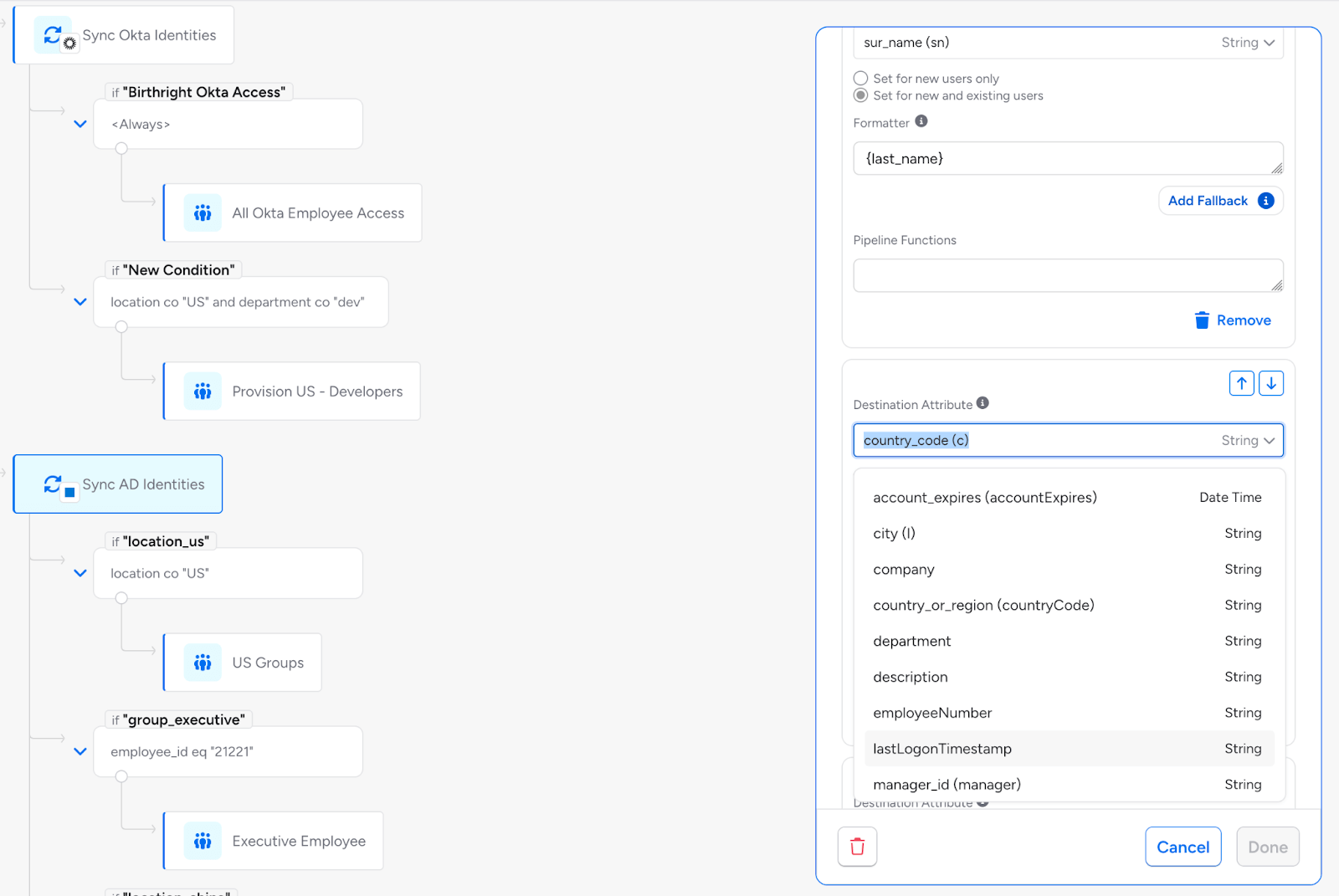
Access Review Creation State Control: Administrators can now select whether workflow-triggered access reviews start as Active (immediately available to reviewers) or Draft (requiring administrator review before launching). This gives you control over review timing when automating access reviews triggered by Lifecycle Management workflows.
Common Transformer Cloning: Duplicate existing attribute transformers to speed up policy configuration. Select any transformer from the Common Transformers table and choose Clone. The creation form opens pre-populated with that transformer’s logic, ready for you to adjust for a new workflow.
Workflow Actions Usability: Clone and delete operations for workflows have moved from primary buttons to the overflow menu (three dots ⋮), reducing visual clutter in the policy editor.
Common Synced Attributes Ordering: Drag and drop to reorder common synced attributes in the policy editor. The order determines priority when multiple sources provide the same attribute, giving you explicit control over which system wins when identity data conflicts.
Boolean Transformer Support: Condition transformers now correctly evaluate boolean values (`true` and `false`) as actual booleans instead of text strings, preventing unexpected workflow behavior when conditions depend on boolean attributes.
Updated Action Type Icons: Each action type in the policy builder now has a distinct icon, making it easier to scan complex workflows and identify provisioning steps at a glance.
Enhanced Identity Details: The Identity Details table now shows all schema attributes, including those with empty values. This enables overriding any property for an identity, and can be useful for handling edge cases, such as setting a `termination_date` override for emergency account deactivations.
Non-Human Identity (NHI) Security
Enhanced Credential and Authentication Discovery
Okta OAuth Token and Credential Discovery: Discover OAuth secrets and machine credentials stored in your Okta tenant. Upon enabling the new Gather Credentials option (disabled by default), Veza now extracts Okta API Tokens, OAuth Application Client Secrets, Refresh Tokens, and Key Credentials used by service integrations.
This reveals which applications have long-lived tokens that could be exploited if compromised, and shows API tokens used for programmatic access to Okta. Learn more about Okta integration.
Salesforce Agentforce and Einstein Bot Discovery: Veza now shows which users can interact with Salesforce AI agents. The Salesforce integration now discovers Agentforce agents and Einstein Bots, maps their service account operators, and shows which users have access through profiles and permission sets. This helps you govern who can deploy or modify automated workflows that act on behalf of your organization. Learn more about NHI Security.
Azure AD/Entra NHI Discovery: Service principals in Azure AD now appear in the NHI Security dashboard with their complete authentication profile. Veza now captures app registration credentials, OAuth2 access tokens, and credential lifecycle metadata, offering centralized visibility into all machine identities across your Azure environment.
AWS IAM Roles Anywhere: Veza now discovers how workloads outside AWS authenticate using IAM Roles Anywhere.
- You can now search and visualize which X.509 certificates are trusted, which trust anchors and certificate revocation lists are configured, and which AWS permission sets these external identities can assume. This helps bridge visibility gaps for on-premises or multi-cloud workloads accessing AWS without traditional IAM users.
GCP Workload Identity Federation Identity Pools: The Azure integration now discovers how identities access GCP resources through federation. The Google Cloud integration now maps Azure AD Enterprise Applications and Azure Managed Identities to GCP Workload Identity Pools, revealing cross-cloud access patterns that might otherwise be invisible in single-cloud security tools.
AWS Identity Center Certificate and OAuth2 Discovery: The AWS integration now discovers X.509 certificates and OAuth2 tokens used with IAM Identity Center. See which certificate-based identities have access to which permission sets, and track trusted token issuers for federated authentication. Learn more about AWS integration.
Okta API Token Relationships: Okta API tokens now appear in Access Graph with clearer ownership attribution, showing user-to-token relationships to help identify who owns each programmatic access credential. API tokens in Okta now appear in their own Access Mechanism layer in Access Graph, positioned before (to the left of) users for clearer visual separation when exploring non-human identity access paths.
HashiCorp Vault KV2 Key-Level Discovery: You can now enable key-level extraction for HashiCorp Vault KV2 secrets engines to see individual key-value pairs as separate entities in the Access Graph. Instead of treating an entire secret path as one resource, you can now visualize access to specific keys within that path. Learn more about HashiCorp Vault.
Veza Integrations
Enterprise Platform Support
Azure Subscription Filters: Administrators can now configure allow and deny lists by subscription ID to control which Azure RBAC and Blob Storage resources Veza extracts. This is particularly useful in large Azure tenants where excluding development or sandbox subscriptions can improve performance and reduce clutter in the Access Graph.
AWS Certificate Manager Support: Veza now discovers X.509 certificates used for AWS authentication. The integration now extracts certificate metadata from AWS Certificate Manager, showing which certificates are used with IAM Roles Anywhere and other AWS services.
AWS OIDC Identity Providers: AWS IAM OIDC identity providers now appear alongside SAML providers, giving you full visibility into how external identities federate into AWS environments via OpenID Connect.
GitLab: The GitLab integration now shows how SAML groups from your identity provider correspond to GitLab roles. This prevents duplicate role assignments in Graph when users and groups are both granted the same permissions.
PingOne: PingOne is now available as a destination type for Custom Identity Mapping Configurations, enabling you to correlate identities from other sources to PingOne accounts.
Oracle Database: Oracle Database integrations now support encrypted connections using either TLS with CA certificates (PEM files) or Oracle Wallet files (.sso). This enables Veza to connect to production Oracle databases that require SSL/TLS encryption. The integration automatically detects connection settings across different Oracle deployment types, including AWS RDS Oracle, Oracle Cloud Autonomous Database, and on-premises installations. You can now upload either a .pem certificate or an Oracle Wallet .sso file during integration configuration.
Cassandra: For Cassandra clusters with dynamic IP addresses or shared certificates, administrators can now optionally disable SSL host verification. Host verification remains enabled by default for security, with the option to disable for deployment architectures where SANs do not match individual node hostnames.
Custom IDP Identity Mapping: Map identities from sources like Active Directory or Okta to your custom identity provider implementations. Custom Identity Mapping configurations now support custom IDPs as destinations, with filtering by IDP type to support different mapping rules for specific providers.
OAA Custom Properties: When building custom applications with the Open Authorization API, custom property names can now include numbers after the first character, such as `level_1` or `tier_2`.
CSV Integration Priority: CSV file uploads through the integration UI now parse faster with automatic prioritization in the processing queue.