News and Highlights from Veza Releases
Welcome to the monthly Veza product update! Veza provides intelligent automation and precise control across the entire identity landscape. This release introduces customizable outlier detection, enterprise integrations for identity lifecycle automation, and expanded coverage for NHI infrastructure and modern AI services.
These enhancements and new capabilities are part of our commitment to helping security teams prevent and respond to identity risks while reducing the operational burden of compliance and access certification. Below you’ll find detailed information on specific updates, along with a summary of release highlights. As always, please contact your Veza support team with questions and feedback.
Release Highlights
Lifecycle Management (LCM)
- Workflow and action controls: Pause or disable specific actions within workflows or entire workflows for safer testing and gradual rollouts; includes visual indicators in the policy editor.
- Send REST Payload action: Trigger custom actions in external applications with configurable REST API calls
- Inline testing: Test attribute formatters directly within the Sync Identities action in the workflow editor for immediate validation of behavior.
- Enterprise integration expansion: MySQL, Oracle Database, PostgreSQL, AWS RDS-managed databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle), SCIM Enterprise Extensions, PagerDuty, and Splunk Enterprise are now supported as target applications for user provisioning and deprovisioning.
Why it matters
Safe workflow testing and expanded integration coverage enable organizations to automate identity lifecycle operations across heterogeneous infrastructure with confidence.
Access Reviews
- Customizable outlier detection: Configure outlier detection using any grouping property from source, destination, or enriched nodes with custom threshold percentages (Early Access).
- Risk Visibility: The Access Review side panel displays all contributing risks for any top-level identity (IdP user) currently under review.
- Better sharing and collaboration through shared links, and improved support for reviewer re-assignment.
- Customizable notification templates for a wider range of event types directly from the Veza UI.
Why it matters
Intelligent risk and outlier detection reduce recertification and review time by surfacing access patterns that deviate from organizational norms.
Non-Human Identity (NHI) Security
- Okta Authorization Server discovery: The Okta integration now discovers Okta Authorization Servers, policies, scopes, claims, and application grants for OAuth and OIDC infrastructure visibility.
- AWS Bedrock Agent relationships: The AWS integration now provides visibility into Bedrock Agent IAM Role relationships for authentication and inherited permissions.
Why it matters
Support for OAuth infrastructure, AI agents, and service accounts enables identification and remediation of over-privileged service accounts.
Access visibility and Access Intelligence
- Query Builder: You can now filter and sort cached search results without the need to run additional queries.
- Access Graph: For quick authorization data insights, graph search now displays entity counts and relationship metrics in your environment.
- Query result enrichment: Get information about linked identities with support for enriched queries that join metadata across multiple sources.
Why it matters
Performance improvements enable security teams to investigate access questions at the pace of modern threats.
New and enhanced integrations
- New integration support for Splunk Enterprise (with Lifecycle Management support), AWS DocumentDB (cluster and database-level discovery), and Database Application (SQL-based custom app modeling).
- AWS visibility enhancements: Root user entity discovery with CloudTrail login tracking, and IAM Role to Local User identity mapping for cross-cloud access paths.
- Bulk configuration: Salesforce now supports CSV upload for custom object configuration, and the Integrations page adds data source state filtering.
Why it matters
Expanded integration coverage and streamlined configuration reduce manual effort to model complex environments in Access Graph.
Access Visibility
Access Graph and Query Builder Usability
- For quick insights into the scale and scope of authorization data in your environment, Access Search and Query Builder landing pages now display current statistics about your Veza Access Graph.
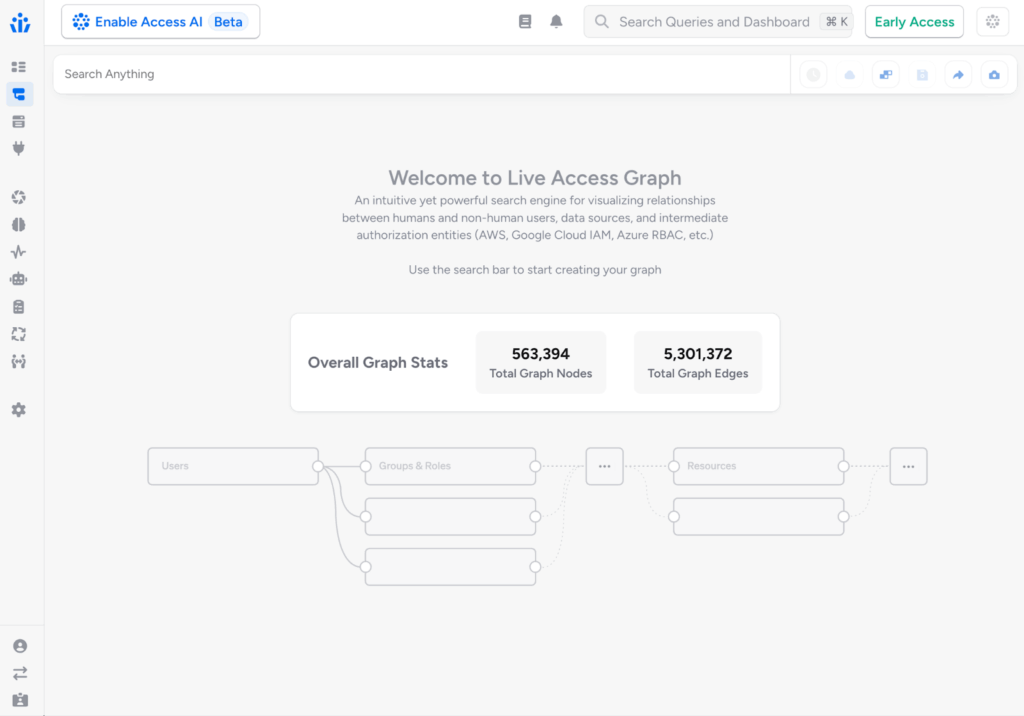
- Query Builder now caches results for faster filtering and sorting, eliminating the need to re-run similar queries while building search conditions.
- Query Builder now supports query result enrichment using additional metadata sources immediately after selecting a source entity type, without requiring destination nodes to be selected first.
- It’s now possible to enrich source nodes using metadata from associated Active Directory Group entity types.
- You can now open a wider range of Access Graph searches directly in Query Builder, enabling better transitions between graph exploration and query creation.
Access Reviews
New Features and Enhancements
- Reviewers can now get insight into unusually rare access granted to users relative to their peers through customizable Outlier Detection for Access Reviews (Early Access). Administrators can configure outlier detection at both global and review-specific levels using any grouping attribute from source, destination, or enriched metadata (not just manager-centric hierarchies), and set custom thresholds. Reviewers can now toggle a filter to focus immediately on access outliers.
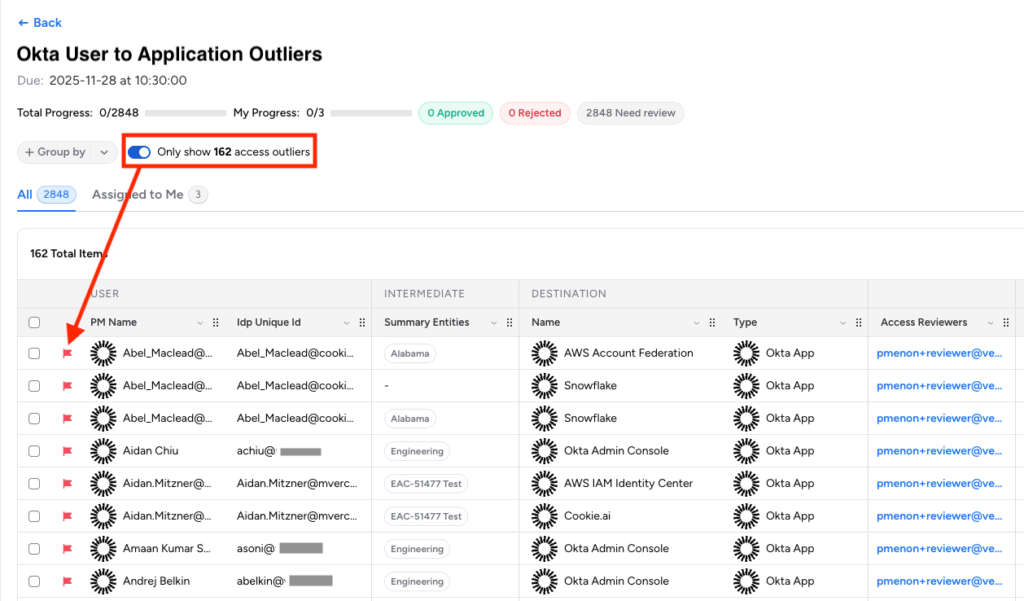
This change enables tailored outlier detection logic specific to your organization’s governance requirements. Outlier Detection is currently available in Early Access for Advanced Access Reviews customers.
- Users can now get quick insights with Access AI for Access Reviews (Early Access) directly in the reviewer interface, including an Access AI-generated explanation of the current review scope, outstanding work, and assigned review items in natural language.
Product Design and Usability Enhancements
- Filter preferences on the Configurations and Reviews tables are now preserved in the URL for easier sharing and team collaboration with shared links to these overview pages.
- Improved support for filtering on enriched attributes from additional metadata sources, such as the linked HRIS Manager Name for a source Okta user.
- Added support for customizing notification templates for additional Access Review event types (Create Access Review, Create Access Review Queued) directly from the Veza UI.
- When reassigning Access Review rows to a different reviewer, reviewers now see a warning that any unsigned approval or rejection decisions will be cleared. The row action log now includes “decision cleared” events for visibility into ownership transfers.
Lifecycle Management (LCM)
Improved Policy Management
- Administrators can now pause or temporarily disable specific actions in workflows, for safer testing and the gradual rollout of workflow changes. This enables workflows to remain active while specific actions are disabled and skipped during workflow execution. When testing policies with a Dry Run, paused actions are always skipped.
- Administrators can now choose to enable or pause entire workflows within Lifecycle Management policies, providing workflow-level control for testing, seasonal policies, or gradual rollouts.
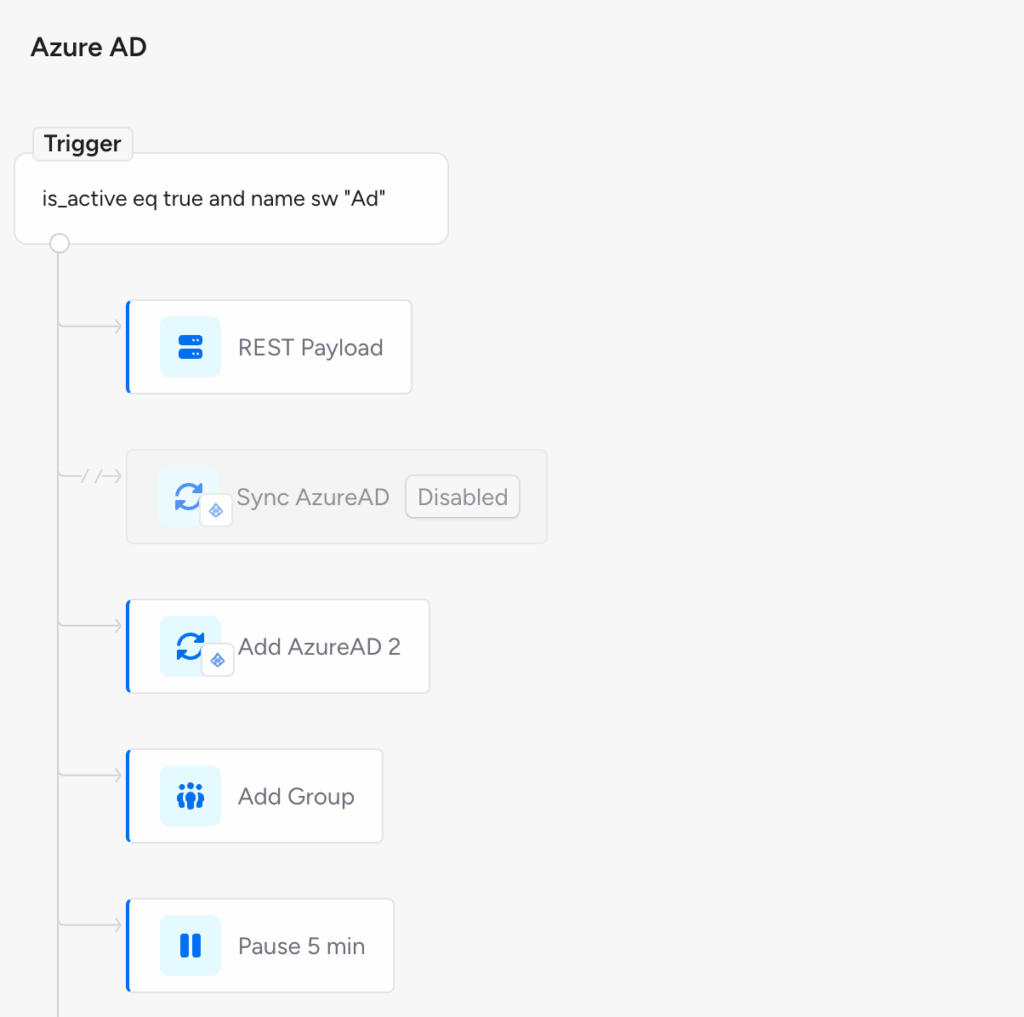
- Disabled workflows are skipped during policy execution and displayed with a visual indicator in the policy editor, for temporary deactivation without deletion. Disabled workflows are still evaluated for Dry Runs initiated from the Veza UI.
- Lifecycle Management policies can now include a Send REST Payload action for customized integration with external workflows and applications. This action is now available in Early Access, enabling integration with downstream systems as part of a workflow. This might include performing additional provisioning or deprovisioning actions, updating database records, or recording events to an external application.
- Send REST Payload can be used to enable notifications and trigger workflows in any system or application that does not natively integrate with Veza Lifecycle Management.
- Administrators can configure custom REST API calls with authentication credentials, URL settings, request payloads, response output mapping, and timeout settings.
Design and Usability Enhancements
- The Workflow editor now supports drag-and-drop reordering of actions across different conditional branches, making it easier to reorganize complex policy logic without needing to redefine actions. This change supports both reordering within the same condition and hierarchical moves between different conditions.
- For Policies configured with both primary and secondary identity sources, the Identities table now supports showing attributes from the active identity source. This feature is currently available in Early Access.
- For immediate feedback on attribute transformations, the Policy Workflow Editor now supports inline testing of formatters while defining workflows.
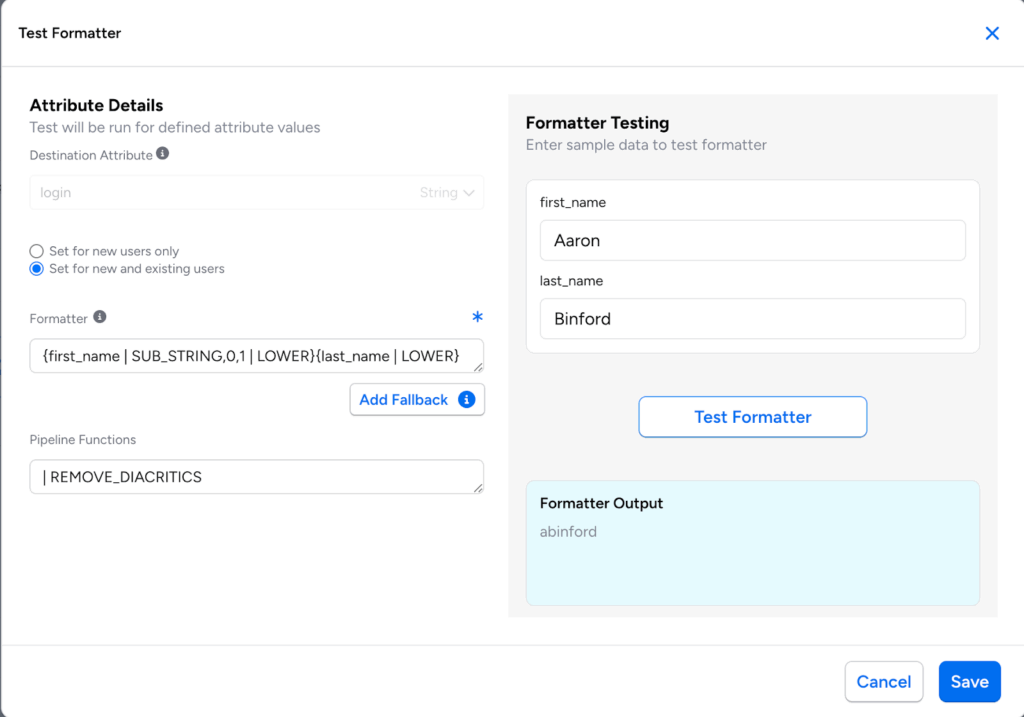
- As part of the Sync Identity action, you can now use formatters to append values to multi-value Active Directory attributes (string lists), without replacing existing values. For more information, see Appending Multi-Value Attribute (Active Directory only).
- When selecting attributes for synchronization, the attribute type is now clearly displayed alongside the attribute name in dropdown menus. This can help determine the required value format (e.g., string, string list, or boolean).
Custom Email Templates
- Lifecycle Management workflows can now implement custom email templates for notifications. Administrators can choose between event-based Notification Templates (existing default behavior) and Custom Email Templates when configuring workflow and action-level notifications.
Enterprise Integrations
- Added target application support for PagerDuty, enabling automated user provisioning (create/modify users), group management (add/remove users from teams), and user deprovisioning (user deletion).
- Target application support for Splunk Enterprise can now automate user identity and access management operations, including account creation, deletion, role assignment, and identity synchronization based on policies and external identity sources.
- Oracle Database can now be enabled as a target application, allowing for automated management of Common Users (root container) and Local Users (PDB-specific). Supported operations include user provisioning with profile assignments, role management (GRANT/REVOKE), and deprovisioning via account lock or user deletion.
- PostgreSQL is now supported as a target application and supports automated user provisioning, access management, and deprovisioning. When Lifecycle Management is enabled for the integration, administrators can now configure workflows to synchronize identity information, manage group memberships, and delete or deprovision identities.
- Veza now supports AWS RDS MySQL, PostgreSQL, and OracleDB as target applications, enabling automated user provisioning, role assignment, and account deprovisioning for managed database services.
- Veza’s SCIM integrations can now automatically fetch SCIM Enterprise Extension Attributes and Custom Extension Attributes from the target server at runtime, enabling Lifecycle Management operations (such as trigger conditions and attribute synchronization) on user and group metadata beyond standard SCIM 2.0 core user attributes.
Non-Human Identity (NHI) Security
- The Okta integration now discovers Okta Authorization Server entities and related policies, expanding Non-Human Identity (NHI) coverage for OAuth/OIDC infrastructure. This enhancement provides visibility into authorization servers, their policies, scopes, claims, and application grants.
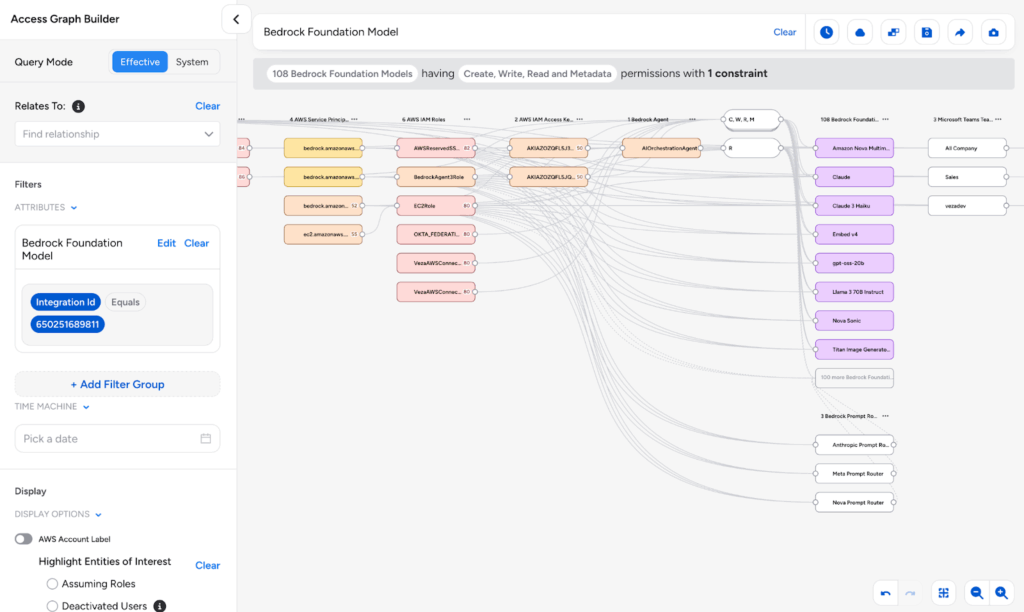
- The AWS integration now discovers relationships between Bedrock Agents and their associated IAM Roles, providing better visibility into how Bedrock Agents authenticate and what permissions they inherit from their execution roles.
- Veza now uses the ServiceNow “identity type” attribute for more accurate classification of service accounts and integration users when detecting non-human identities.
Veza Integrations
New Integrations
- Splunk Enterprise: Added a new integration for Splunk Enterprise, providing visibility into access management and authorization within Splunk deployments. The integration discovers users, roles, groups, and their associated capabilities, including LDAP and SAML-federated identities. Lifecycle Management support is also available for automated user provisioning.
- AWS DocumentDB: The AWS integration now supports Amazon DocumentDB (with MongoDB compatibility), providing two-tier discovery for both cluster infrastructure and database-level permissions. Veza discovers DocumentDB clusters via AWS APIs and, when database credentials are configured, extracts users, roles, and granular MongoDB-style permissions.
- Database Application: Added a new OAA-based integration for importing identity and authorization data from SQL database tables. The Database Application integration supports Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL/MariaDB, Oracle Database, and PostgreSQL, enabling Veza to model custom applications by reading user, group, role, and resource data directly from database query results.
Enhancements
- Salesforce Custom Objects CSV Upload: The Salesforce integration now supports CSV import for bulk configuration of custom objects. Previously, enabling custom Salesforce objects required manual entry in a dropdown field, which became cumbersome when managing large numbers of objects. Administrators can now upload a CSV file containing Salesforce Object API names to configure all desired custom objects at once.
- AWS IAM Role to OAA Local User Identity Mapping: Added support for identity mapping between AWS IAM Roles and OAA Custom Application Local Users. This enables modeling cross-cloud access patterns in Access Graph, where AWS workloads (Lambda, EC2) assume IAM Roles that federate to local users in on-premises or custom systems.
- AWS Root User Support: The AWS integration now discovers AWS account root users as distinct entities, providing visibility into root account access and activity. This includes discovery of root user entities with account-level metadata, tracking of the 10 most recent root user login events via CloudTrail, and visibility into root user authentication details (source IP, MFA usage, and login timestamps).
- Data source state filtering: The Integrations page now supports filtering data sources by their enabled or disabled state, making it easier to identify and manage inactive integrations.
- LDAP: Added support for additional LDAP user properties, active_user_property and inactive_user_property. In Veza, the LDAP User IsActive status is now determined with the improved logic:
- All users are defaulted to isActive = true
- If active_user_property is false, isActive = false
- If inactive_user_proprety is true, isActive = false