Access governance is more than a buzzword in today’s business world–it’s a vital strategy for keeping your company’s digital spaces secure by controlling who can see and use your company’s information and tools.
However, the move to the cloud, application sprawl, and the complexity of new access models have led to a much more complicated access governance process. Additionally, with businesses moving faster than ever, IT teams need to somehow quickly evaluate and grant access while still enforcing secure access policies and adhering to compliance.
This guide will explain what access governance is, why it’s important for your organization, and how it differs from other types of access management. It will also highlight the benefits of Intelligent Access, and some best practices for it in your business.
What is Access Governance?
Access governance is a discipline businesses use to ensure that individuals have appropriate access to company resources. It involves overseeing and regulating who can view and use various parts of an organization’s information systems and data.
Simply put, access governance helps ensure that employees only have access to the information they need for their jobs–and nothing more.
User Access Governance vs Data Access Governance
Access governance is made up of two key components: managing access for users and managing access to data:
- User Access Governance: This is about managing who can access what within an organization’s systems and networks. It involves overseeing and controlling user rights and privileges across various IT resources. User access governance ensures that each employee or user has the appropriate level of access necessary for their role. It includes tasks like granting access when a new employee is hired, updating access when an employee’s role changes, and revoking access when someone leaves the company. The goal is to prevent excessive or inappropriate access that could lead to security risks.
- Data Access Governance: Data access governance concentrates on the “what.” It’s about managing how data within an organization is accessed and used. This includes ensuring that sensitive or confidential data, like customer information or proprietary business data, is only accessible to authorized individuals. Data access governance involves classifying data based on sensitivity, monitoring how data is used, and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. The aim is to protect critical data from unauthorized access and misuse, thus safeguarding the organization’s data assets and compliance posture.
Why Access Governance is Important
Access governance plays a crucial role in today’s ever-changing business world. Here’s why:
Reducing Complexity
The digital transformation has led to an explosion in the number of systems and applications organizations use. More precisely, the move to cloud computing and the increase in software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications have significantly expanded the types and number of systems an average enterprise uses.
Today, the average enterprise might use 364 SaaS apps and 1,295 cloud services, each with its own access controls and permissions. This “app sprawl” leads to “access sprawl,” making it increasingly difficult for security and identity teams to manage and understand access across all different systems effectively.
Access governance simplifies this complexity by providing a centralized framework for managing these varied access models.
Improving Efficiency
With the sheer volume of applications, access points, and identities (thanks to the proliferation of service accounts, third-party users, and machine users) manually managing enterprise permissions is no longer feasible for security and identity teams. Access governance streamlines this process through automation, enabling quicker responses to access requests, role changes, and employee turnover.
Boosting Security
As the volume and complexity of access increase, so does the surface area for potential cyber threats. In a world where 75% of breaches occur through the misuse of identities, access governance is critical for security.
Effective access governance plays a crucial role in securing an organization’s digital assets. By enforcing policies like the principle of least privilege, access governance ensures that users have only the access necessary for their roles, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Staying Compliant
Compliance with various regulations (like SOX, SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, and more) is a major concern for organizations. Ultimately, non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and legal issues.
Access governance helps organizations maintain compliance by employing tools to monitor, control, and report on access under these regulatory requirements.
Minimizing Risk
Over time, excess permissions can lead to privilege creep, where employees end up with more access rights than their roles require. This not only increases the risk of insider threats but also serves as an extensive attack surface for external threats.
Access governance helps systematically reduce these risks by providing a comprehensive view of access rights and usage within organizations. By proactively managing these risks, access governance plays an essential role in protecting against external and internal threats and safeguarding the organization’s assets and reputation.
Access Governance vs Identity Access Management vs Identity Governance and Administration
Terms like access governance, Identity Access Management (IAM), and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) are sometimes used interchangeably in cybersecurity and identity management. However, while they all aim to secure digital identities and access rights, each plays a different role.
- Access Governance: Access governance focuses on overseeing and regulating who has access to an organization’s IT systems and data. It’s about ensuring that the right people have the right level of access to the right resources at the right time. This includes managing user permissions across different systems, applications, and data stores. Access governance is crucial for security, compliance, and minimizing organizational risks. It often involves auditing and reporting on access rights, ensuring that they align with policies and regulations.
- Identity Access Management (IAM): IAM is a framework that combines business processes, policies, and technologies to manage digital identities and control user access to critical information within organizations. It encompasses components such as authentication, role-based access controls (RBAC), and the management of digital identities for both humans and devices. IAM systems, which can be deployed on-premises, via cloud-based services, or in a hybrid model, include technologies like Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and Privileged Access Management (PAM).
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Privileged access management focuses on managing and monitoring privileged or elevated access to an organization’s most valuable information and resources. (e.g., admin accounts and some service accounts). Cybercriminals often target privileged accounts because they hold the keys to the kingdom—access to critical systems, sensitive data, and the ability to change system configurations. PAM gives visibility into who uses privileged accounts, limits the number of users with access to administrative functions, and analyzes privileged user activity to identify anomalies.
- Identity Governance and Administration (IGA): IGA is another critical component of IT security, focusing on automating and securing digital identities across users, applications, and data to optimize operational efficiency and address security and compliance risks. IGA tackles key business challenges by reducing operational costs by automating access certifications, access requests, password management, and provisioning. It enhances security by providing centralized visibility into access rights, quickly identifying and remedying policy violations and inappropriate access. It also supports compliance with regulations like SOX, HIPAA, and GDPR by ensuring proper controls are in place through consistent management processes, RBAC, and automated policy enforcement.
However, while IAM, PAM, and IGA all serve important functions, they also have certain limitations.
For instance, IAM focuses on securing initial access points through user authentication–they don’t extend their capabilities into access control and management post-authentication. So while they are effective for verifying user identities and securing entry points, they don’t provide detailed insights or controls over the actions users can perform.
Similarly, PAM tools are specialized for overseeing privileged accounts, such as those of system administrators, but often lack the broader oversight needed for other user categories and their diverse interaction levels with various applications and data. Though PAM solutions can monitor specific accounts within their scope, they fail to catch privileged permissions across all identities–creating a blind spot within your full identity attack surface.
Traditional IGA solutions, often designed with on-premise architectures in mind, might struggle to adapt to the complexity and dynamism of modern, cloud-based IT environments. They aim to manage and govern user access but may encounter blind spots, particularly in understanding granular permissions across varied digital landscapes.
This limitation becomes more pronounced considering the contemporary IT environment’s nature, characterized by an extensive array of cloud services, SaaS applications, and data stores, each with its unique access control mechanisms.
Such environments demand a more holistic approach to access governance, one that can seamlessly navigate the intricacies of different access control systems like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC). Traditional tools do not provide comprehensive coverage across these platforms, leading to gaps in access governance.
Access Governance Best Practices
For access governance to work, there are some best practices every organization should follow. These steps help reduce your potential attack surface, prevent policy violations, and improve decision-making across the business.
- Take an “Assume Breach” Mentality
Adopting an “assume breach” mentality is crucial in today’s digital landscape, where cybersecurity threats are rampant. This approach acknowledges that data breaches are not just possibilities but inevitabilities. Gartner has found that 80% of organizations have had some sort of incident related to identity in the last 12 months, with the global average cost of a data breach at $4.45 million in 2023–a 15% increase over 3 years.
Organizations must operate under the assumption that their systems can and will be breached at some point. This mindset encourages proactive measures in security planning rather than reactive responses post-incident. If you know you’ll get breached, you’ll start figuring out how to limit the damage.
- Document Access Governance Policies
Clearly documenting access governance policies is crucial for ensuring consistency and compliance. These policies should detail the procedures for granting, reviewing, and revoking access and define roles and responsibilities within the access governance framework.
Proper documentation is not only key for internal governance but also critical during audits, since it demonstrates the organization’s commitment to maintaining structured and compliant access governance practices.
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege
The principle of least privilege is fundamental in access governance, requiring that individuals only have access to the information and resources necessary for their job functions. This minimizes the risk of accidental or malicious misuse of sensitive data.
Though the principle of least privilege sounds simple enough, applying it in the real world is increasingly complicated as the scale and complexity of hybrid- and multi-cloud deployments rise.
While it may not be possible to sustain “perfect” least privilege at all times, any improvement makes you safer from both internal and external threats. Regularly reviewing and updating access rights helps ensure no unnecessary privileges are granted and any changes in roles or responsibilities are reflected promptly in access permissions.
- Conduct User Access Reviews
Regular user access reviews are a critical component of effective access governance. These reviews involve auditing user access rights to ensure they remain appropriate over time. This process helps identify and rectify any discrepancies, such as redundant or outdated access privileges, thereby maintaining the integrity and security of the system.
User access reviews also play a vital role in compliance with regulatory standards.
From PCI DSS to SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR, and SOX, each set of regulations demands rigorous control over who can access what within an organization.
- Collect Access Intelligence
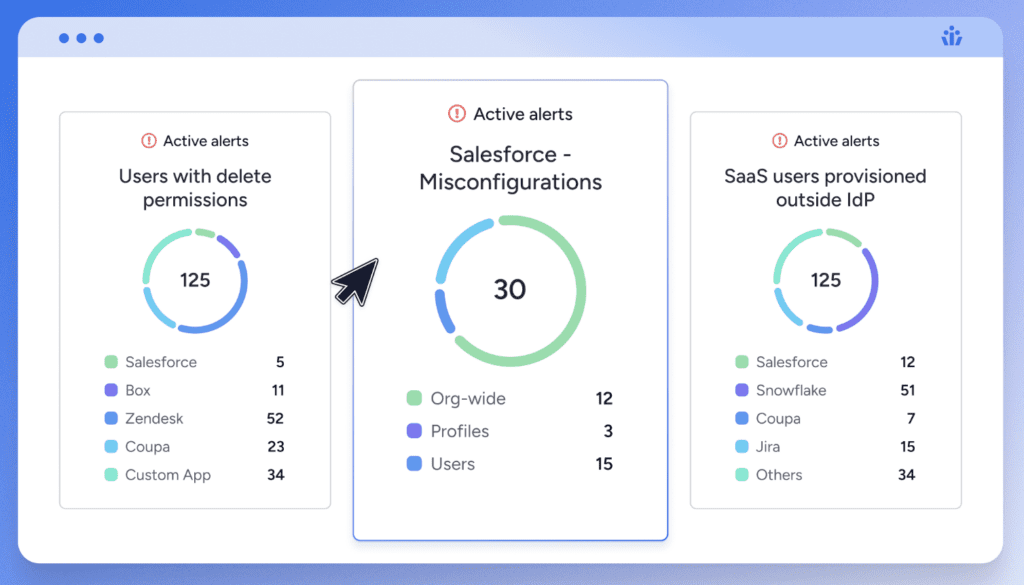
Access intelligence involves analyzing data about how access rights are deployed and consumed within an organization. Security and identity teams need analytics that monitor access patterns, identifying unusual or unintended access.
Access intelligence can help proactively identify potential security risks and ensure access governance policies are addressing the organization’s needs.
Streamlined Access Governance & Decision Making Through Intelligent Access
Every day, companies accumulate excessive permissions in the normal course of granting access. All of these accumulated permissions become open doors for attackers. Without proper access governance, it’s difficult to keep track of who has access to what, making it almost impossible to detect whether these permissions are still necessary or have turned into potential liabilities.
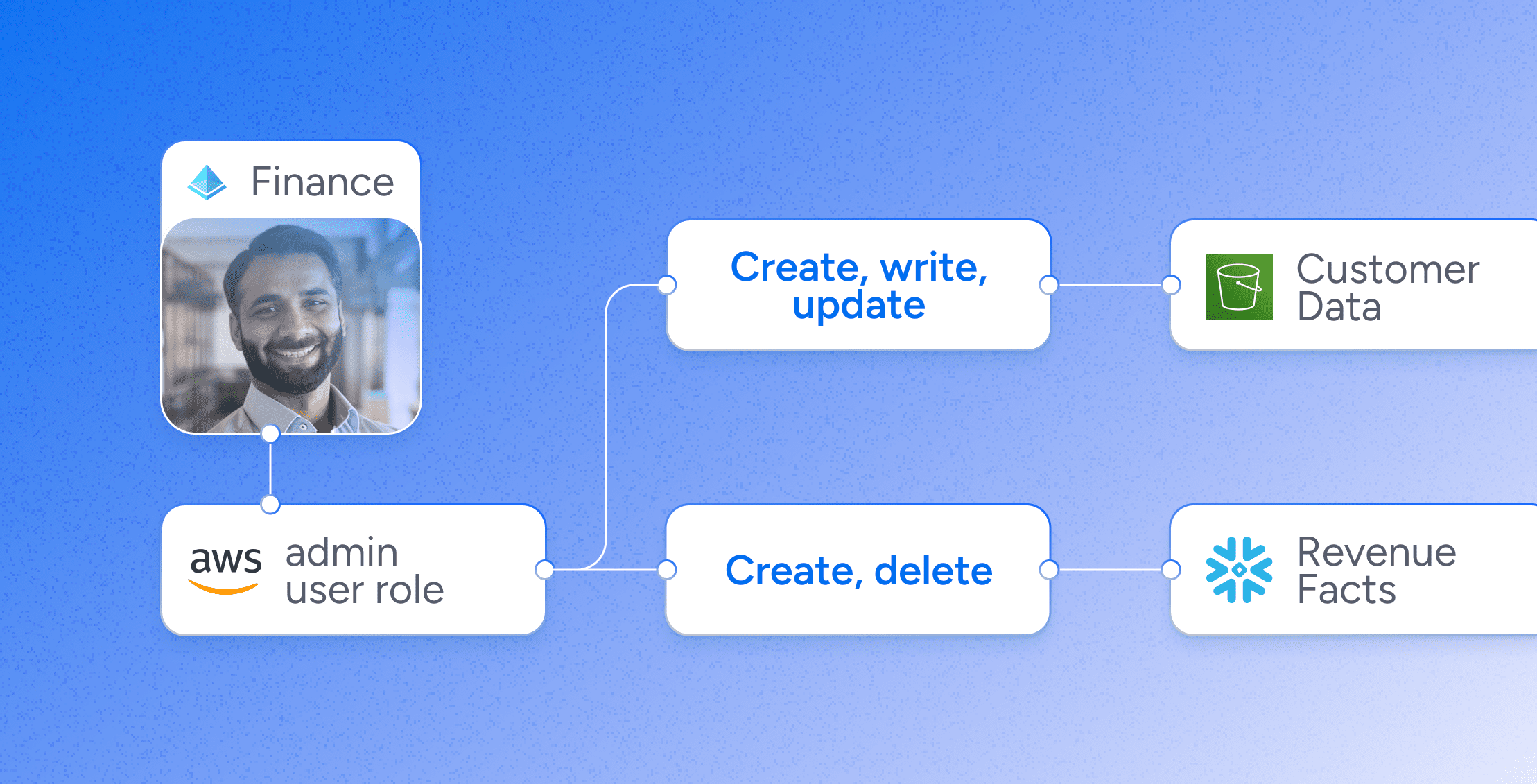
Veza is revolutionizing how organizations manage digital identities and access control, preparing businesses for current and future security challenges. Powered by the Authorization Graph, the platform delivers visibility and control of permissions so that organizations finally
Veza ensures access governance keeps up with business speed, automatically adjusting permissions according to security policies for all identities and systems.
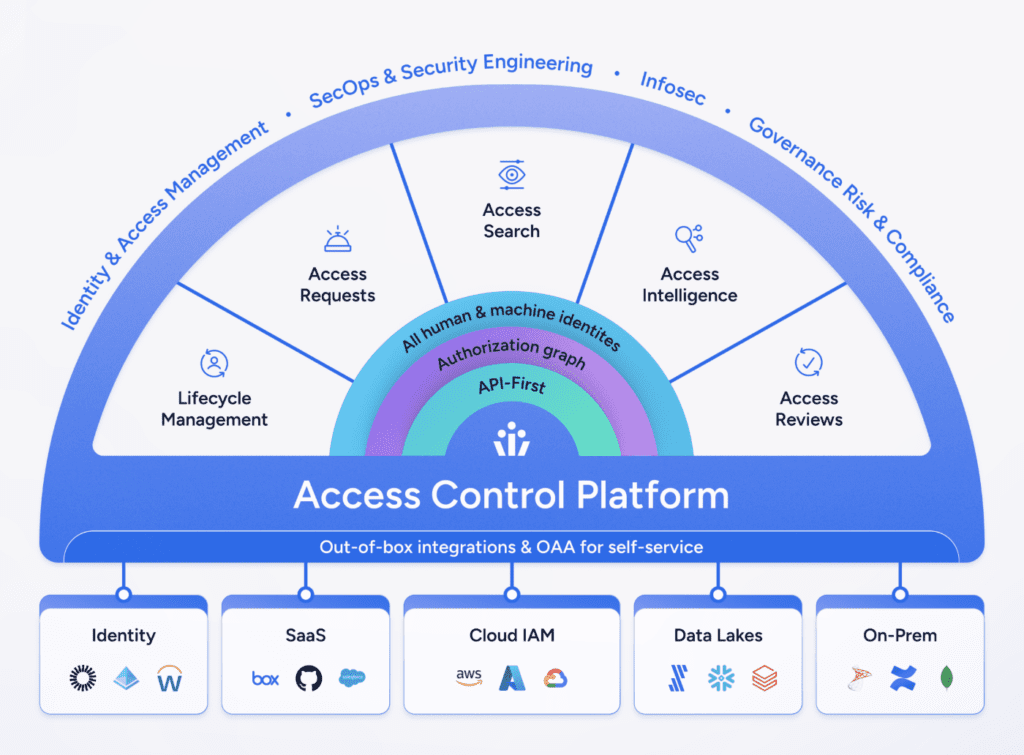
Intelligent Access is based on five key tenets:
- All Systems: Quick connection to any enterprise system, providing a full view of access.
- All Identities: Monitors all identities, human and machine, for a complete access overview.
- True Permissions: Goes beyond basic user roles to understand detailed app and resource permissions.
- Standardized Understanding: Translates complex permissions into clear business terms.
- Automated Decision-Making: Automates monitoring and resolving access issues, enhancing efficiency.
Veza, powering Intelligent Access, goes beyond traditional user-centric models to address risky permissions and policy violations. It ensures secure access across all enterprise systems for both human and machine identities.
With Veza, companies can visualize who has access to what, manage identity risks efficiently, and automate access reviews for better collaboration. It analyzes authorization data from various sources, presenting an easy-to-understand overview of permissions across your enterprise.
Organizations concerned about identity-based attacks, data breaches, ransomware, insider threats, and easing the work of compliance would do well to invest in modern access governance.
Ready to Turn Insight into Action?
Access governance isn’t just a concept—it’s a strategic imperative. Whether you’re just getting started or actively evaluating solutions, Veza offers the depth, clarity, and control you need to modernize access for the way business gets done today.
- 👉 Just exploring? What is Intelligent Access?
A quick primer on how access governance has evolved—and why “who has access to what” is no longer good enough. - 🔍 Need to go deeper? A Practitioner’s Guide to Intelligent Access
A field manual for identity teams. Learn how to operationalize least privilege across SaaS, infrastructure, and data systems—without getting buried in manual reviews. - 🎥 Want a quick look? Watch the Veza SaaS Access Governance Demo
Real product. Real use cases. Real fast. See how Veza gives you the visibility and control your current IAM stack can’t.
🤝 Ready to get hands-on? Schedule a Demo
Let’s get specific. Tell us your biggest access challenge—we’ll show you exactly how Veza can solve it.