As a seasoned security practitioner and the Chief Security & Trust Officer at Veza, I have witnessed firsthand the challenges organizations face in their journey towards zero trust. The rapid adoption of cloud technologies, the explosion of data, and the proliferation of human and machine identities have made implementing a robust zero trust strategy more complex than ever. However, one aspect remains clear: identity security is the cornerstone of a successful zero trust implementation.
Understanding the Challenges
CISOs and their teams are all too familiar with the obstacles that come with implementing zero trust. The sheer volume and complexity of permissions, coupled with the constant proliferation of identities, can be overwhelming. Managing access across a multitude of platforms, applications, and data repositories often leads to over-provisioned access, unmanaged identities, and increased risk of data breaches.
Zero trust architecture is summarized in the figure below, highlighting the key areas of focus required,
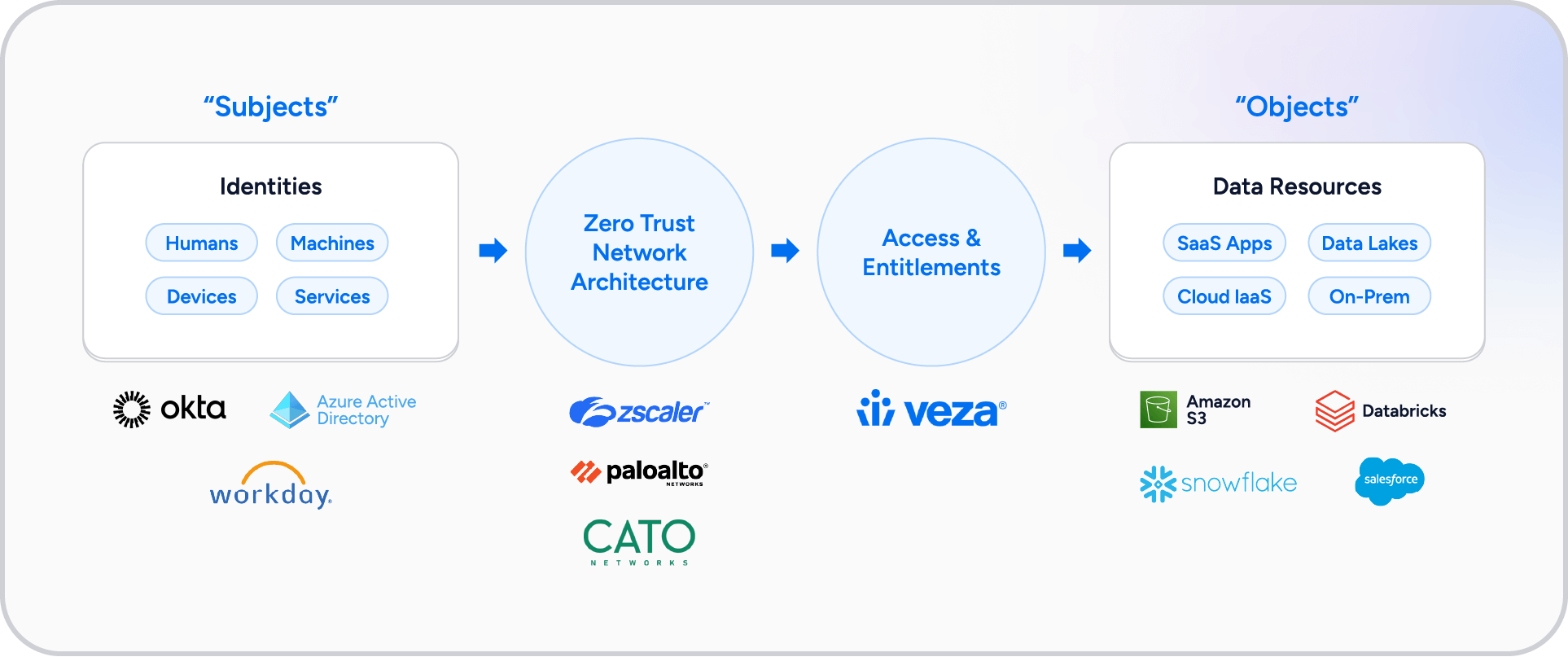
To effectively implement zero trust, organizations must address several critical aspects of identity security:
- Real-time monitoring and control of privileged access
- Enforcing least privilege across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS platforms
- Managing user entitlements in SaaS applications
- Securing access to data platforms
- Streamlining identity governance processes
- Managing non-human identities, such as service accounts and machine identities
Addressing these challenges requires a unified view of all identities and permissions across the enterprise, as well as the ability to translate system-specific permissions into easily understandable descriptions and map them to individual identities.
The Vital Role of Identity Security
Security practitioners must recognize that identity security is the foundation upon which a comprehensive zero trust strategy is built. By ensuring that access is granted based on the principle of least privilege and continuously verified, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
To effectively implement zero trust, organizations need granular visibility and control over identities and permissions. This visibility and control enable us to continuously monitor access, enforce intelligent access controls, and automate remediation processes. By leveraging these capabilities, we can maintain a strong security posture while reducing the burden on our security and identity teams.
Partnering for Zero Trust Success
Navigating the complexities of identity security and achieving zero trust objectives requires the right tools and strategic partnerships. As a practitioner, I understand the importance of having a platform that simplifies the complexity of identity security and provides the necessary visibility and control to enable zero trust success.
When evaluating potential partners, look for solutions that offer:
- A unified view of all identities and permissions across the enterprise
- Continuous monitoring and intelligent access controls
- Automated remediation capabilities
- Support for a wide range of platforms, applications, and data repositories
- Scalability to meet the needs of your growing organization
By partnering with the right provider, organizations can gain a strategic ally in their zero trust journey and confidently navigate the challenges of identity security.
Conclusion
Implementing zero trust is a complex but critical undertaking for organizations in today’s digital landscape. Identity security plays a vital role in enabling zero trust success, providing the foundation for granular access control and continuous monitoring.
As security practitioners, it is our responsibility to recognize the challenges and prioritize identity security in our zero trust initiatives. By doing so, we can foster enduring trust, uphold our organization’s reputation, and secure our digital future.